The origin of cosmic rays has been a mystery since their discovery nearly a century ago. But new images from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope may bring astronomers a step closer to understanding the source of the Universe’s most energetic particles. The images show where supernova remnants emit radiation a billion times more energetic than visible light. “Fermi now allows us to compare emission from remnants of different ages and in different environments,” said Stefan Funk, an astrophysicist at the Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology (KIPAC).
Cosmic rays are made up of electrons, positrons and atomic nuclei and they constantly bombard the Earth. In their near-speed-of-light journey across the galaxy, the particles are deflected by magnetic fields, which scramble their paths and mask their origins. When cosmic rays collide with interstellar gas, they produce gamma rays. While instruments can infer the presence of cosmic rays by looking for the glow of gamma ray emissions, so far, no specific sources have been located.
“Understanding the sources of cosmic rays is one of Fermi’s key goals,” said said Funk, who presented the new images and findings at the American Physical Society meeting in Washington, D.C. on Monday.
Fermi’s Large Area Telescope (LAT) mapped billion-electron-volt (GeV) gamma rays from three middle-aged supernova remnants — known as W51C, W44, and IC 443 — that were never before resolved at these energies. (The energy of visible light is between 2 and 3 electron volts.) Each remnant is the expanding debris of a massive star that blew up between 4,000 and 30,000 years ago.
In addition, Fermi’s LAT also spied GeV gamma rays from Cassiopeia A (Cas A), a supernova remnant only 330 years old. Ground-based observatories, which detect gamma rays thousands of times more
energetic than the LAT was designed to see, have previously detected Cas A.
“Older remnants are extremely bright in GeV gamma rays, but relatively faint at higher energies. Younger remnants show a different behavior,” explained Yasunobu Uchiyama, a Panofsky Fellow at SLAC. “Perhaps the highest-energy cosmic rays have left older remnants, and Fermi sees emission from trapped particles at lower energies.”

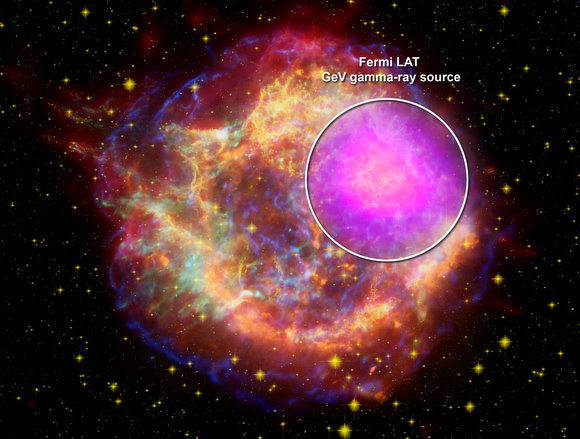
Fermi mapped GeV-gamma-ray emission regions (magenta) in the W44 supernova remnant. The features clearly align with filaments detectable in other wavelengths. This composite merges X-ray data (blue) from the Germany/U.S./UK ROSAT mission, infrared (red) from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope, and radio (orange) from the Very Large Array near Socorro, N.M. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration, NASA/ROSAT, NASA/JPL-Caltech, and NRAO/AUI
In 1949, physicist Enrico Fermi — for whom the Fermi telescope was named –suggested that the highest-energy cosmic rays were accelerated in the magnetic fields of gas clouds. In the decades that followed,
astronomers showed that supernova remnants are the galaxy’s best candidate sites for this process.
Young supernova remnants seem to possess both stronger magnetic fields and the highest-energy cosmic rays. Stronger fields can keep the highest-energy particles in the remnant’s shock wave long enough to speed them to the energies observed.
The Fermi observations show GeV gamma rays coming from places where the remnants are known to be interacting with cold, dense gas clouds.
“We think that protons accelerated in the remnant are colliding with gas atoms, causing the gamma-ray emission,” Funk said. An alternative explanation is that fast-moving electrons emit gamma rays as they fly past the nuclei of gas atoms. “For now, we can’t distinguish between these possibilities, but we expect that further observations with Fermi will help us to do so,” he added.
Either way, these observations validate the notion that supernova remnants act as enormous accelerators for cosmic particles.
“How fitting it is that Fermi seems to be confirming the bold idea advanced over 60 years ago by the scientist after whom it was named,” noted Roger Blandford, director of KIPAC.
Source: Fermi/Sonoma State University